MAC and IP are the addresses that uniquely defines a device and a connection in a network. A MAC address is a number assigned to the NIC card by the manufacturer. IP address is a number assigned to the connection in a network. The basic difference between MAC address and IP address is that a MAC address uniquely identifies a device that wants to take part in a network.
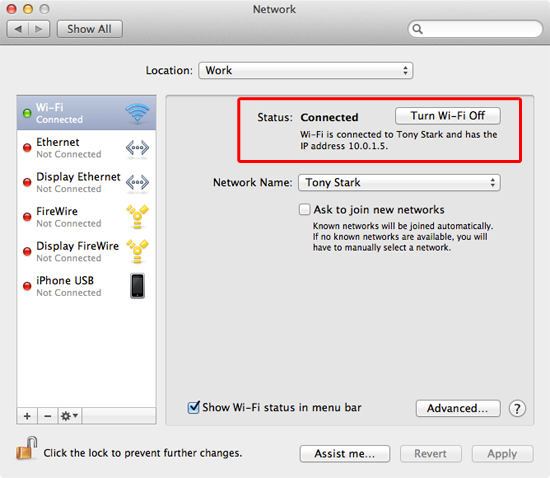
If your computer is connected to both a local network and the Internet, it will have an internal IP address signed by a local network and external IP address, which is the address of your Internet connection. If you are setting up a network or sharing files, the IP address is required. In this article, we show a number of ways to find a Mac IP. The IP address will display. Click the network icon (may look like a computer or Wi-Fi signal) in the task tray. Go to Network settings. Click Ethernet Change adapter options. Or click Status Change adapter options. Highlight and right click on Ethernet, go to Status - Details. The IP address will display. Find your computer’s name and network address on Mac. If other people want to locate your Mac on the network, they need to know your computer’s name or network address. Your Mac has several identifiers that people may look for on the network: computer name, local hostname (or local network name), and network address. Static IP address – this will never vary, and can be considered a perpetual internet address. Dynamic IP address – this is a provisional address that is allocated each time a computer or device connects to the internet. The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a binary number used to specify particular computer network adapters.
Ip Address For This Computer Mac
On the other hand, an IP address uniquely defines a connection of a network with an interface of a device. Let us study some other differences between MAC address and IP address with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: MAC address Vs IP address
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | MAC | IP |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Media Access Control Address. | Internet Protocol Address. |
| Purpose | It identifies the physical address of a computer on the internet. | It identifies connection of a computer on the internet. |
| Bits | It is 48 bits (6 bytes) hexadecimal address. | IPv4 is a 32-bit (4 bytes) address, and IPv6 is a 128-bits (16 bytes) address. |
| Address | MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer of NIC card. | IP address is assigned by the network administrator or Internet Service Provider. |
| Retrieve Address | ARP protocol can retrieve MAC address of a device. | RARP protocol can retrieve IP address of a device. |
Definition of Mac Address

Address that uniquely defines a hardware interface is called MAC (Media Access Control) Address. MAC address is purchased by the manufacturer, producing interface hardware and assign the MAC addresses sequentially to the interface hardware as they are produced. MAC address is burned into the ROM of Network Interface Card (NIC). NIC is an interface hardware that is used by the computer to become a part of a network.
MAC address is a 48-bit hexadecimal address. The format of a MAC address is MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS, where MM:MM:MM is a 3-byte address of the manufacturer. On the other hand, SS:SS:SS is a serial number of NIC card. MAC Address of each computer on a network is unique. When you change or replace the NIC card of your computer, your MAC address also gets changed.
MAC address is used at the data link layer of OSI/TCP/IP model. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a protocol used to receive MAC address of a device.
Definition of IP Address
The address provided to a connection in a network is called IP (Internet Protocol) address. IP address does not uniquely identify a device on a network but, it specifies a particular connection in a network. IP address is provided by the administrator of the network or by Internet Service Provider (ISP).
IP address identifies both a network and the host on that network. IP address is used while routing as it specifically identifies a network connection. If your computer is on two networks so, it will have two IP addresses.
IPv4 address is 32-bit address whereas IPv6 is 128-bit address. Your IP address will get changed each time you connect to the network as it is dynamically allocated to your device when it participates in the network. IP address for a particular connection in a network can be retrieved by RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol).
Key Differences Between MAC Address and IP Address
- The full form of MAC address is Media Acess Control whereas, the full form of IP address is Internet Protocol address.
- The IP address identifies a connection to a device in a network. On the other hand, Mac address identifies a device participating in a network.
- MAC address is 48 bits (6 bytes) hexadecimal address whereas, IP address has two versions, IPv4 a 32-bit address and IPv6 a 128-bit address.
- MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer of interface hardware. On the other hand, IP address is assigned by the network administrator or Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- ARP protocol retrieves the MAC address whereas RARP protocol retrieves IP address.
Conclusion
MAC and IP address both are equally required when a device wants to communicate with another device in a network.
Related Differences:
IP Address
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a rational numerical address which is allocated to every single computer and computer device that is a member of a given Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)-based network.
The IP address is the main element on which the networking architecture is made—no network occurs without it. An IP address is a relevant address that is used to distinctly classify every node in the network. Because IP addresses are relevant, they can be altered. They are like addresses in a city because of the way the IP address provides the network node a location, so that it can connect with other nodes or networks—just like a mail is sent to friends.
-Address-on-a-Computer-Step-23.jpg)
Parts of an IP Address
The numbers in an IP address are broken down into 2 parts:
- The network part indicates which networks the address pertains to
- The host part identifies the specific location
An IP Address is the most essential element in the networking development which connects the various disparate parts of the World Wide Web into what we call the internet. The IP address is a numeric address, which is specified for every single instance with regards to any computer communication network that makes use of the TCP/IP communication procedures.
Standards for IP Address
There are 2 standards for IP addresses:
- IP Version 4 (IPv4) – composed of 4 sets of numbers from 0 to 255, divided by 3 dots. There are 28X4 probable IPv4 addresses. There are 3 classes of IPv4 address sets that can be recorded through the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC):
- Class C – composed of 256 IP addresses (123.123.123.xxx, where xxx is from 0 to 255)
- Class B – composed of 65,536 IP addresses (123.123.xxx.xxx)
- Class A – composed of 16,777,216 IP addresses (123.xxx.xxx.xxx)
- IP Version 6 (IPv6) – composed of 8 sets of 4 hexadecimal digits, divided by colons. There are 3.4 x 1038 probable IPv6 addresses.
Static vs. Dynamic IP Address
- Static IP address – this will never vary, and can be considered a perpetual internet address.
- Dynamic IP address – this is a provisional address that is allocated each time a computer or device connects to the internet.
MAC Address
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a binary number used to specify particular computer network adapters. These numbers, also known as hardware addresses or physical addresses, are either installed in the network hardware during the manufacturing process, or are saved in firmware, and intended to never be altered.
Some refer to them as Ethernet addresses, but Wi-Fi and Bluetooth networks also make use of MAC addressing.
Format of a MAC Address

Conventional MAC addresses are composed of 12-digit hexadecimal numbers and are usually written as follows:

- MMM.SSS.SSS
- MM-MM-MM-SS-SS-SS
- MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS
They are 48 bits or 6 bytes.
Prefix refers to the first 6 digits or first 24 bits and is identified with the adapter manufacturer. Each vendor registers and acquires MAC prefixes as allocated by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Vendors often obtain many prefix numbers identified with various products they create and sell.
The last 6 digits of a MAC address serve as an identification number for the specific device in question. For devices made with the same vendor prefix, each is assigned with their own specific 24-bit number. Hardware from different vendors may turn out to share the same device section of the address.
Some kinds of networks require 64-bit addresses like the Zigbee wireless home automation.
Ip Address For Mac Computer
MAC vs. IP Address Relationship
TCP/IP networks use both MAC and IP addresses but for different purposes.
Ip Address For Mac Address
| MAC Address | IP Address |
|---|---|
| Fixed to the device’s hardware | Can be altered depending on the device’s TCP/IP network configuration |
| Works at Layer 2 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) | Works at Layer 3 of the OSI |